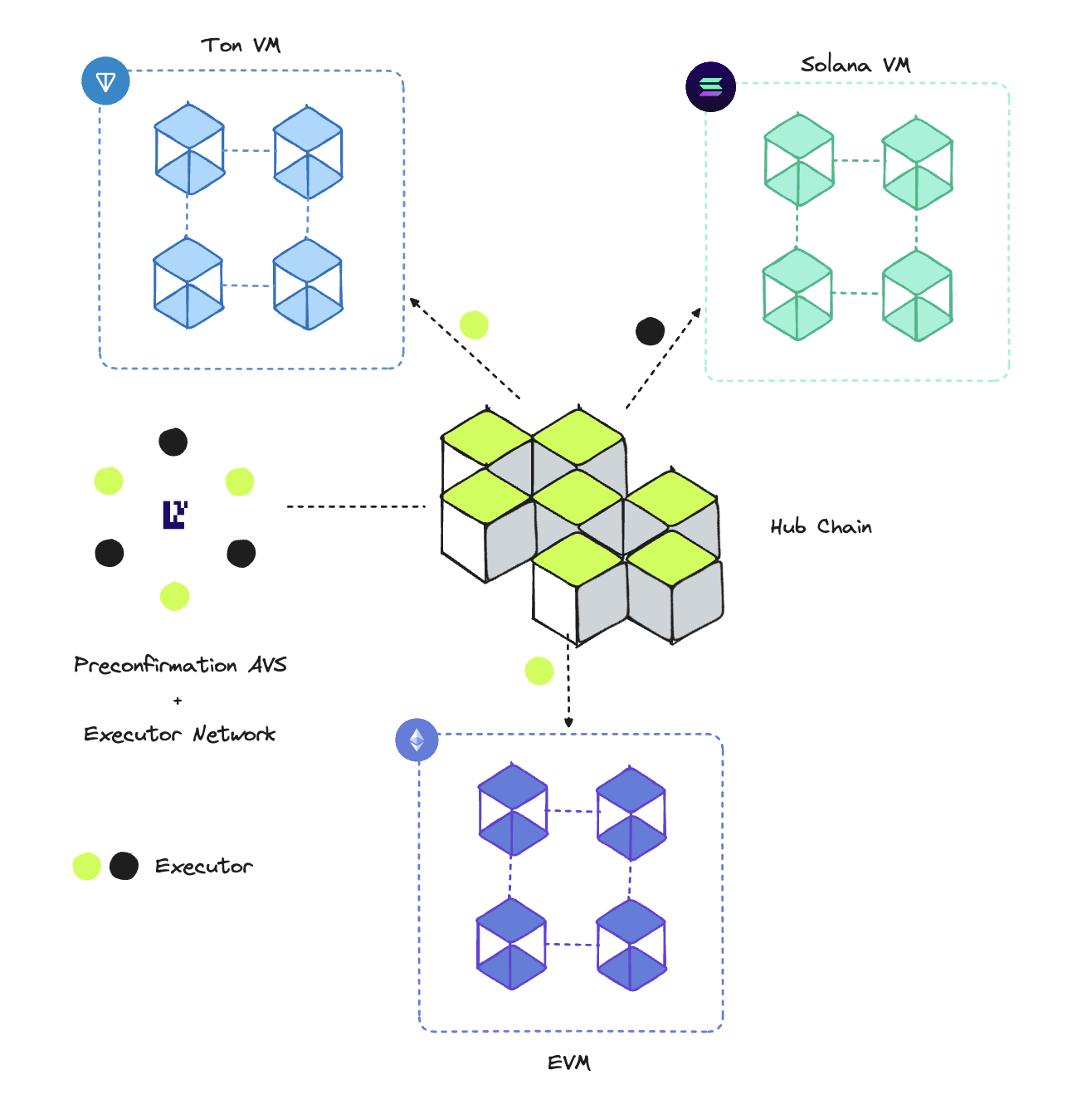
Skate's Infrastructure
- Skate’s Hub Chain: The central hub that handles all logic processing and stores the application state.
- Skate AVS: An AVS deployed on Eigenlayer that facilitates the secure delegation of restaked ETH to Skate’s Executor Network. It serves as the primary source of truth, ensuring that Executors perform the required actions on destination chains.
- Executor Network: A network of executors responsible for executing actions as defined by the application. Each application has its own set of executors.
User flow
Skate is primarily intent powered and each intent encapsulates key information that expresses what a user wants to perform while also defining the necessary parameters and boundaries. Users will only be required to sign intents through their own native wallet and will only interact from that chain, creating a user native environment.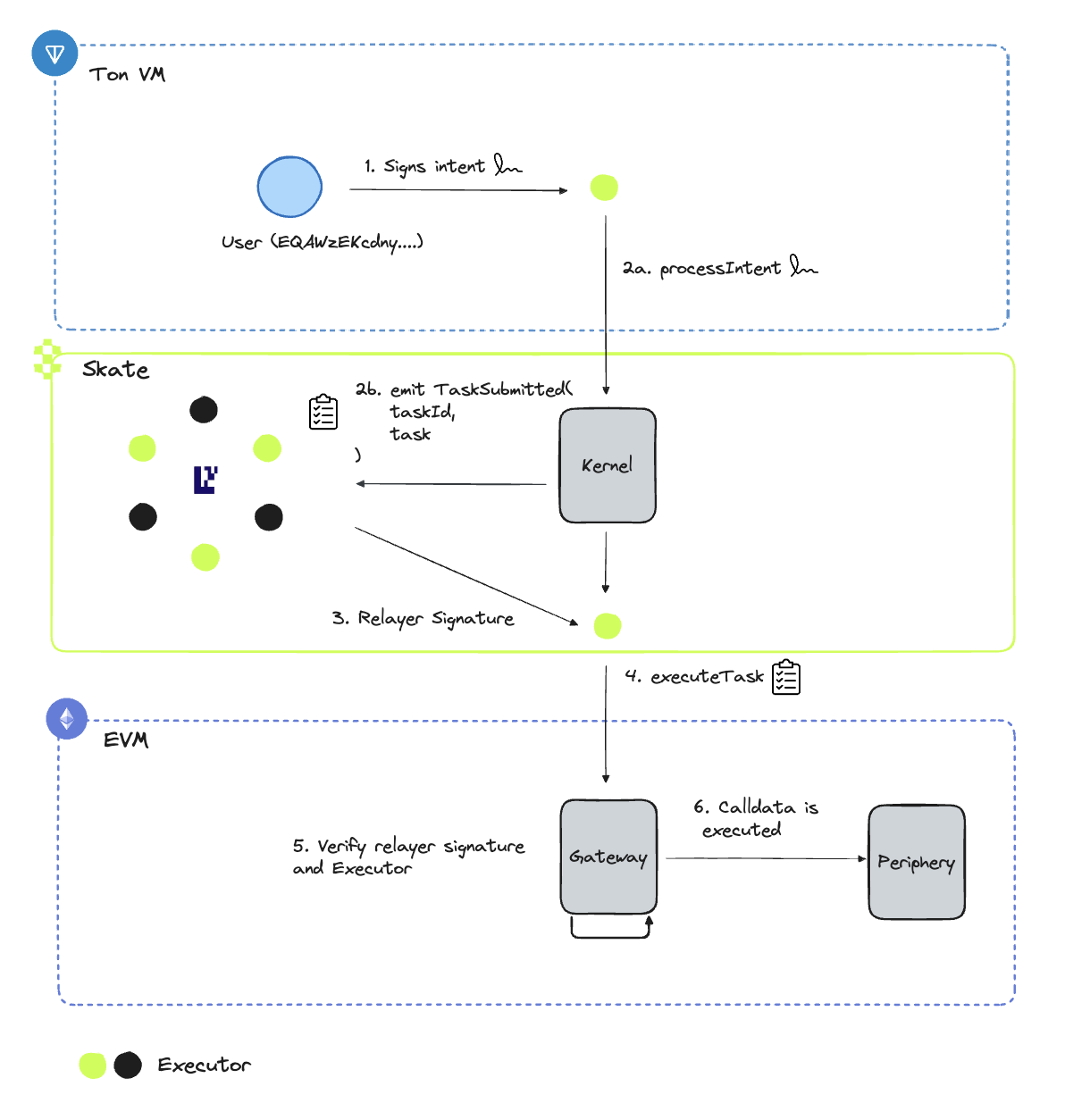
Skate's User Flow
- User will initiate action on by signing an intent on TON/Solana/EVM.
- Executor receives the intent and call processIntent on Skate. This creates a task that encapsulates key information for Executors for task execution. This also emits a TaskSubmitted event.
- AVS validators will be actively listening for TaskSubmitted events and will verify the contents of each task. Upon achieving quorum in our AVS, the relayer will issue a signature that is required for task execution
- Executor calls executeTask on Gateway contract
- Gateway contract will verify that task was validated by AVS through the issuance of a valid relayer’s signature before function call defined in task can be performed.
- Function calldata is executed and intent is marked as complete.

